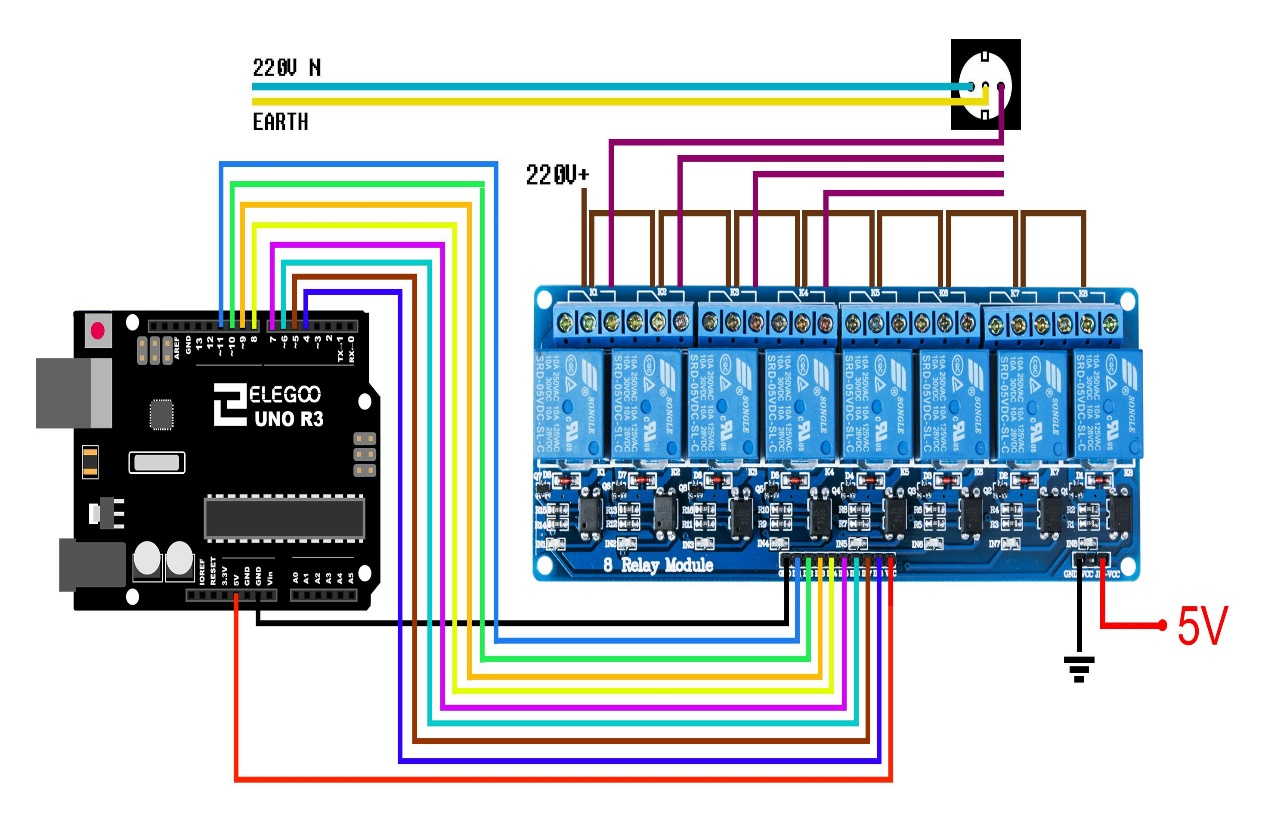
¶ Description
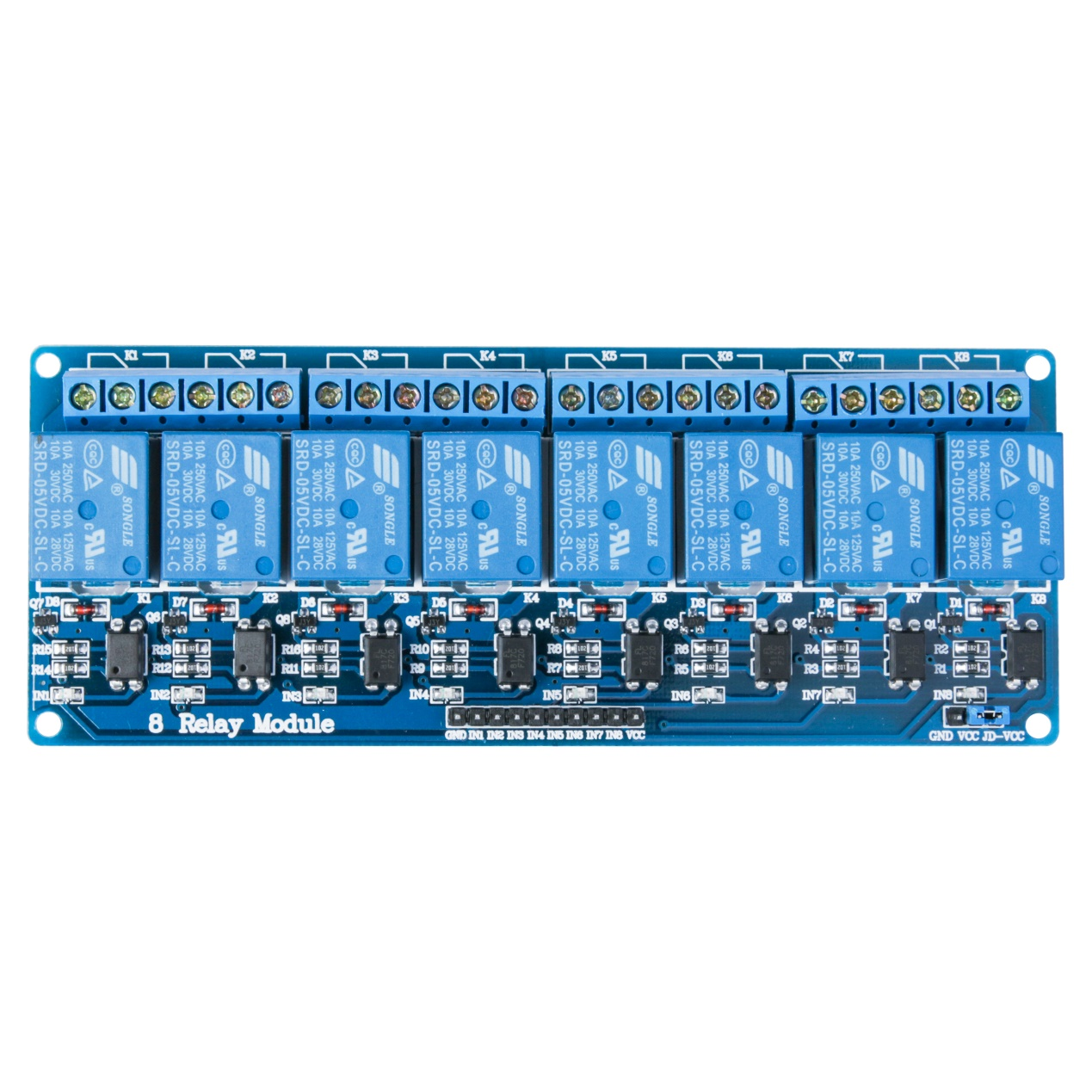
The relay module is an electrically operated switch that allows you to turn on or off a circuit using voltage and/or current much higher than a microcontroller could handle. There is no connection between the low voltage circuit operated by the microcontroller and the high power circuit. The relay protects each circuit from each other.
The each channel in the module has three connections named NC, COM, and NO. Depending on the input signal trigger mode, the jumper cap can be placed at high level effective mode which ‘closes’ the normally open (NO) switch at high level input and at low level effective mode which operates the same but at low level input.
¶ Specifications
- On-board EL817 photoelectric coupler with photoelectric isolating anti- interference ability strong
- On-board 5V, 10A / 250VAC, 10A / 30VDC relays
- Relay long life can absorb 100000 times in a row
- Module can be directly and MCU I/O link, with the output signal indicator
- Module with diode current protection, short response time
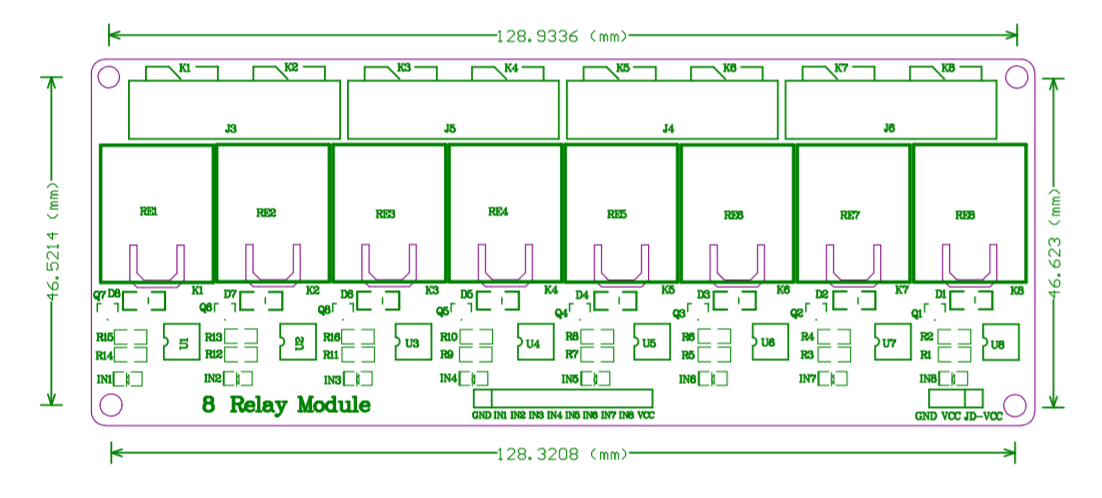
- PCB Size: 72mm x 51.7mm
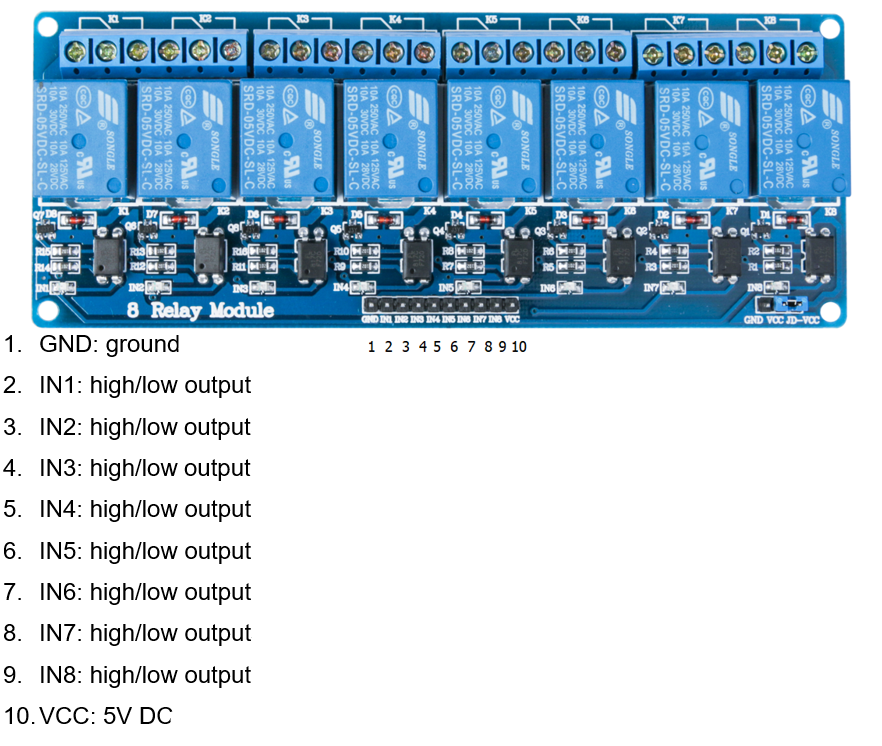
¶ Pin Configuration
¶ Module dimension drawing
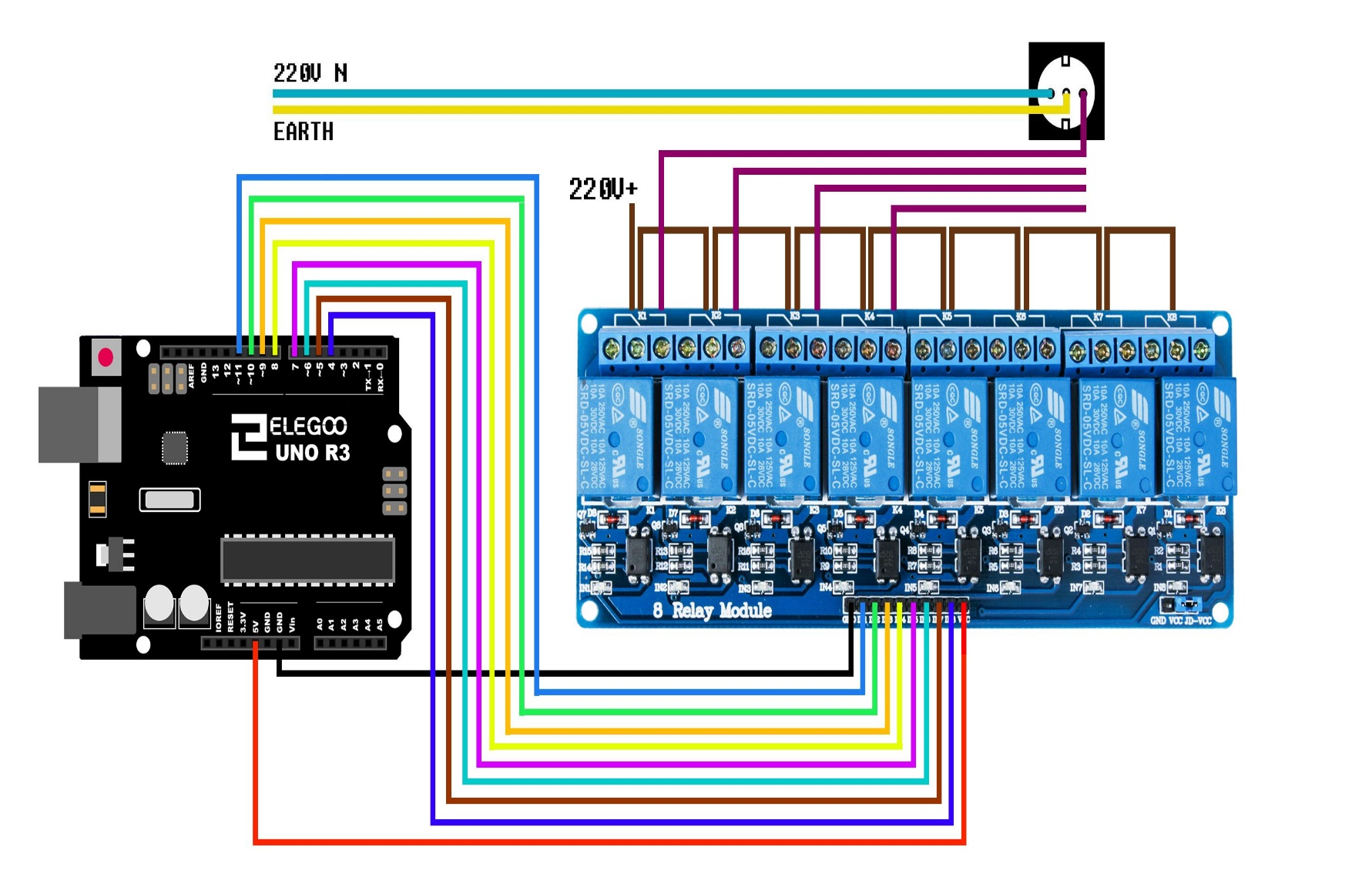
¶ Wiring Diagram
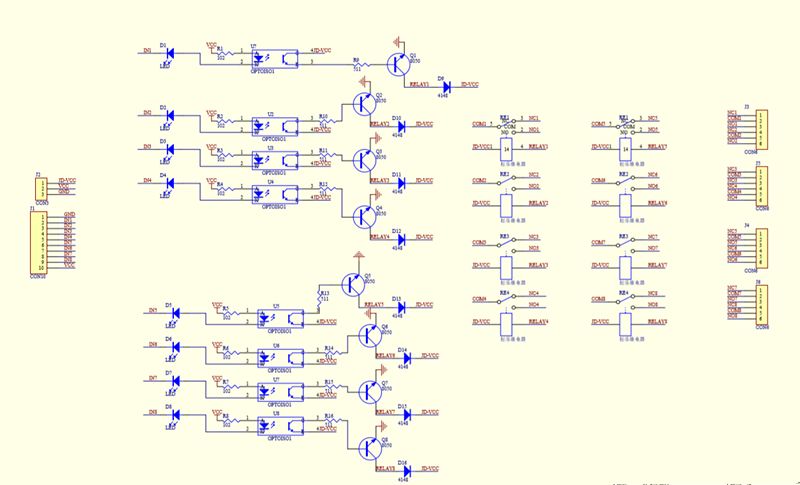
¶ Schematic Diagram
¶ Sample Sketch
void setup()
{ pinMode(11,OUTPUT);
pinMode(10,OUTPUT);
pinMode(9,OUTPUT);
pinMode(8,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{ digitalWrite(11,LOW);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(10, LOW);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(8, LOW);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(11, HIGH);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(10, HIGH);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(9, HIGH);
delay(4000);
digitalWrite(8, HIGH);
delay(4000);
}
¶ How to Test
The components to be used are:
- Microcontroller (any compatible arduino)
- 4 channel 5V 10A relay module
- Pin connectors
- USB cable
- Connect the components based on the figure shown in the wiring diagram using pin connectors. VCC and DJ-VCC pin is connected to the 5V power supply, GND pin is connected to the GND, IN1 and IN2 and IN3 and IN4 pins are connected to the digital I/O pin. Pin number will be based on the actual program code.
- After hardware connection, insert the sample sketch into the Arduino IDE.
- Using a USB cable, connect the ports from the microcontroller to the computer.
- Upload the program.
¶ Testing Results
The figures below shows an alternate switching of the two relays every 4 seconds. A tick sound and a red LED would be observed.
¶ What does the jumper cap do when it connects to DJ-VCC?
Serves to power the part of the relays with the same Vcc of the opto-isolated part. If you want to separate the power supplies, remove the jumper and connect the external power supply between JD and GND without connecting the Arduino GND.
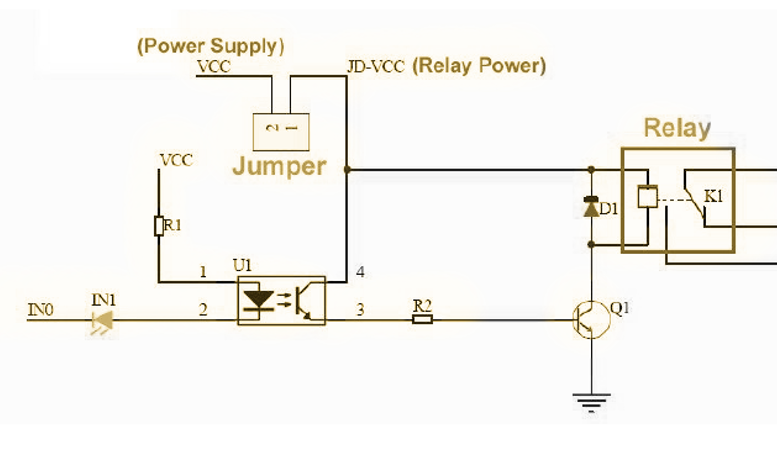
After removing the jumper cap, you need to power the jd-vcc separately as shown below: