| Categories | English Full Name | Introduction | Figure Legends |
| printer | Neptune 2 | Marlin system, printing volume: 220X220X250mm | |
| Neptune 2S | Marlin system, printing volume: 220X220X250mm | ||
| Neptune 3 | Marlin system, printing volume: 220X220X280mm |
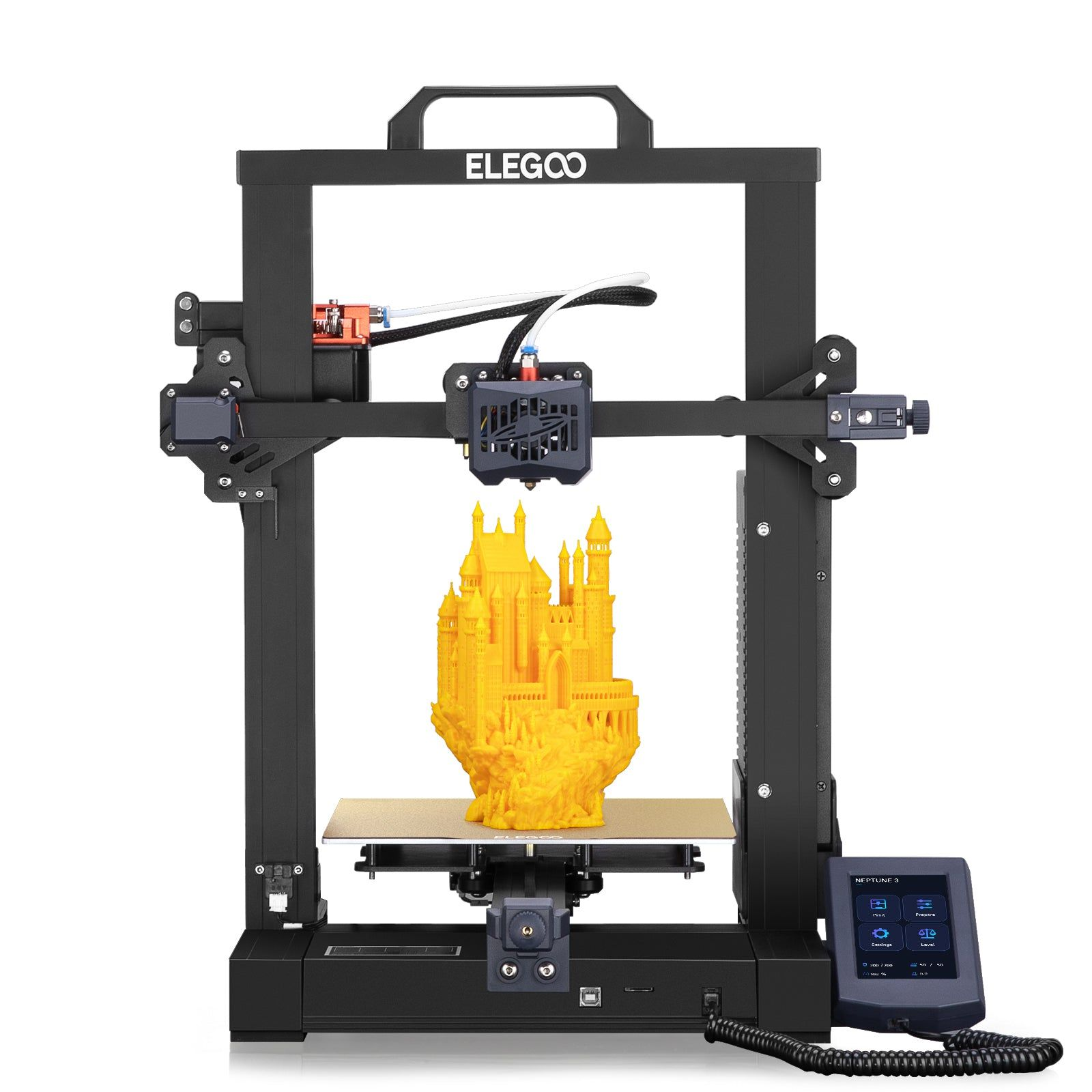 |
|
| Neptune 3 Pro | Marlin system, printing volume: 225x225x280mm | ||
| Neptune 3 Plus | Marlin system, printing volume: 320x320x400mm | ||
| Neptune 3 Max | Marlin system, printing volume: 420x420x500mm | ||
| Neptune 4 | Klipper system, printing volume: 225x225x265mm | ||
| Neptune 4 Pro | Klipper system, printing volume: 225x225x265mm | ||
| Neptune 4 Plus | Klipper system, printing volume: 320x320x385mm | ||
| Neptune 4 Max | Klipper system, printing volume: 420x420x480mm | ||
| printing head | direct extruder | The direct extruder is near the nozzle. It can feed the filament into the nozzle. With short distance between extruder and nozzle, the printer is compatible with various filament and become the most popular type. |
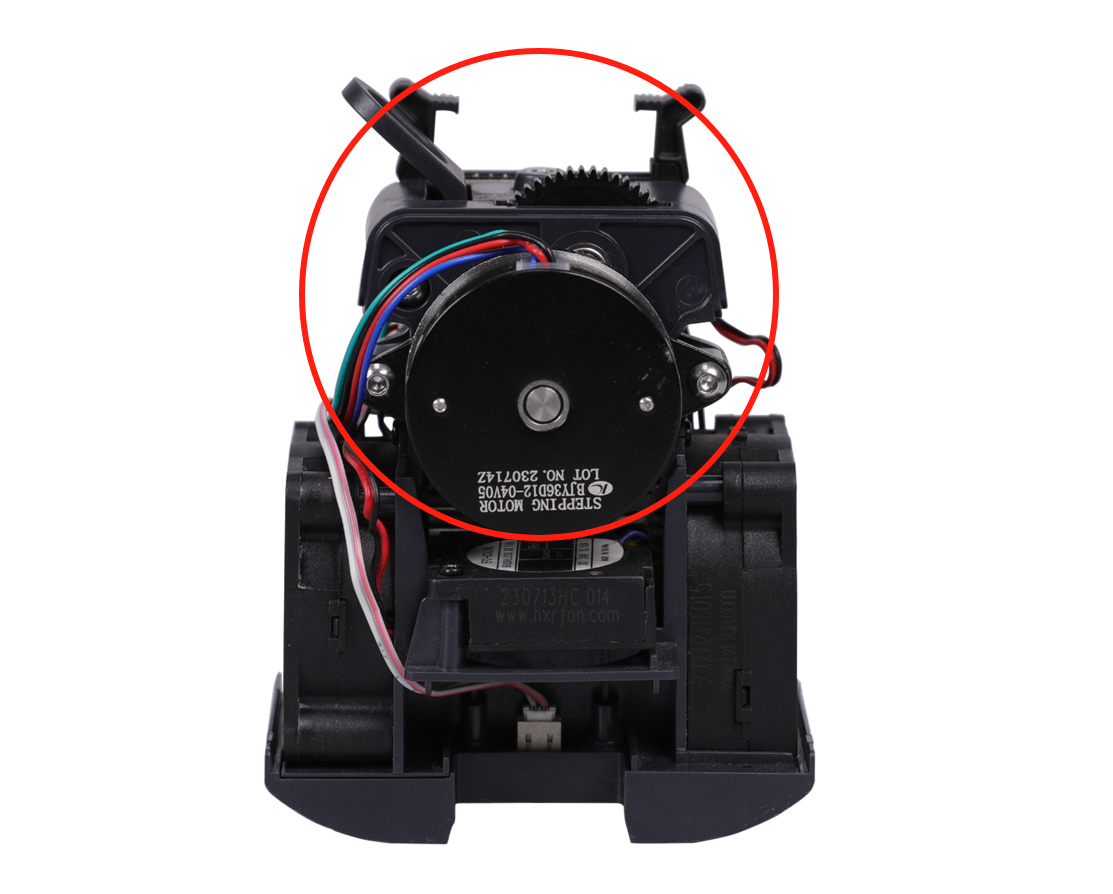 |
| extruder motor | The extruder motor can energize the gear to feed the filament into the nozzle. (Neptune 4 series has circular stepper motor with diameter of 36 mm) |
 |
|
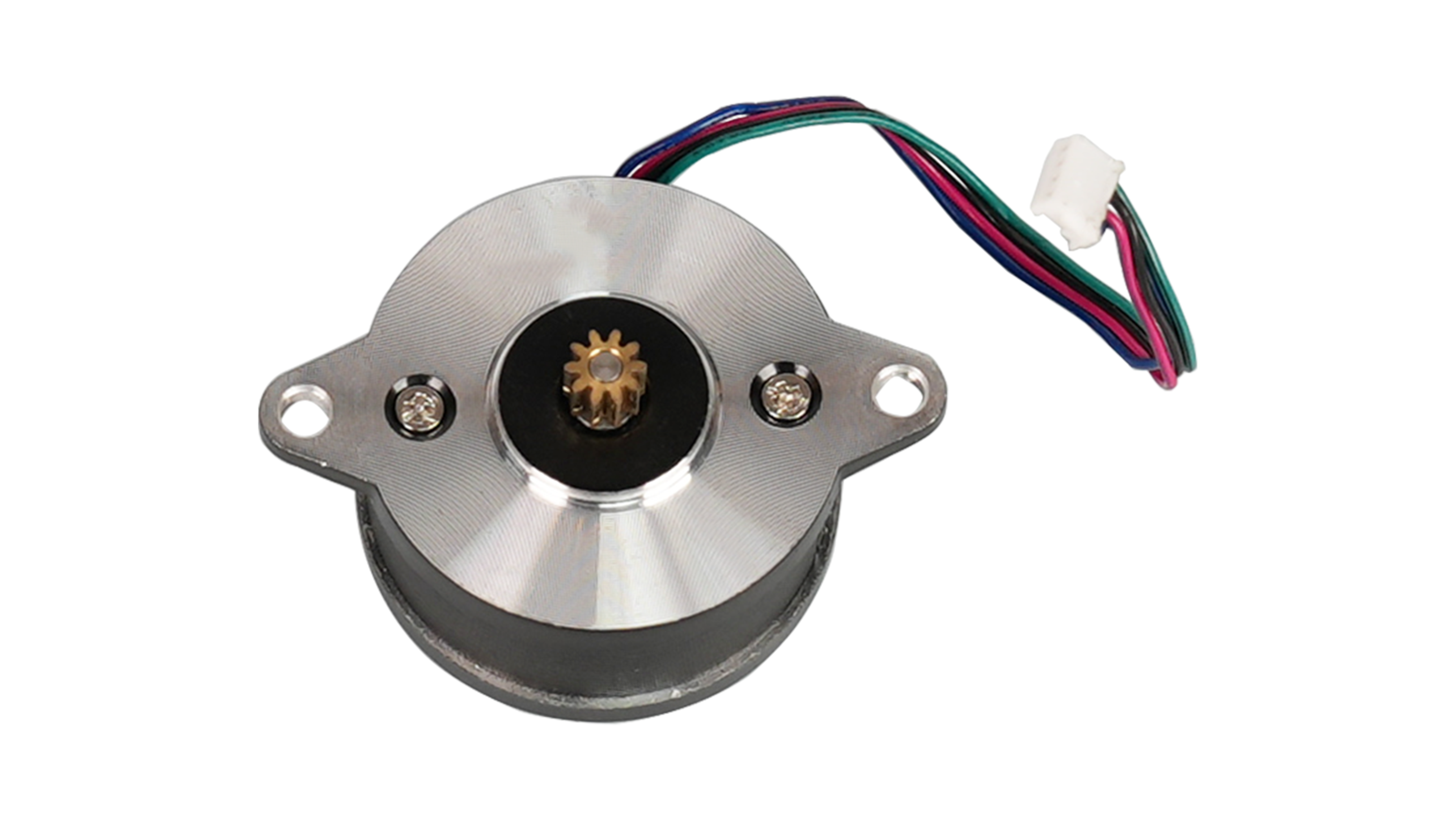
| The extruder motor can energize the gear to feed the filament into the nozzle. (Neptune 3 pro has circular stepper motor with flange diameter of 42mm) |
 |
||
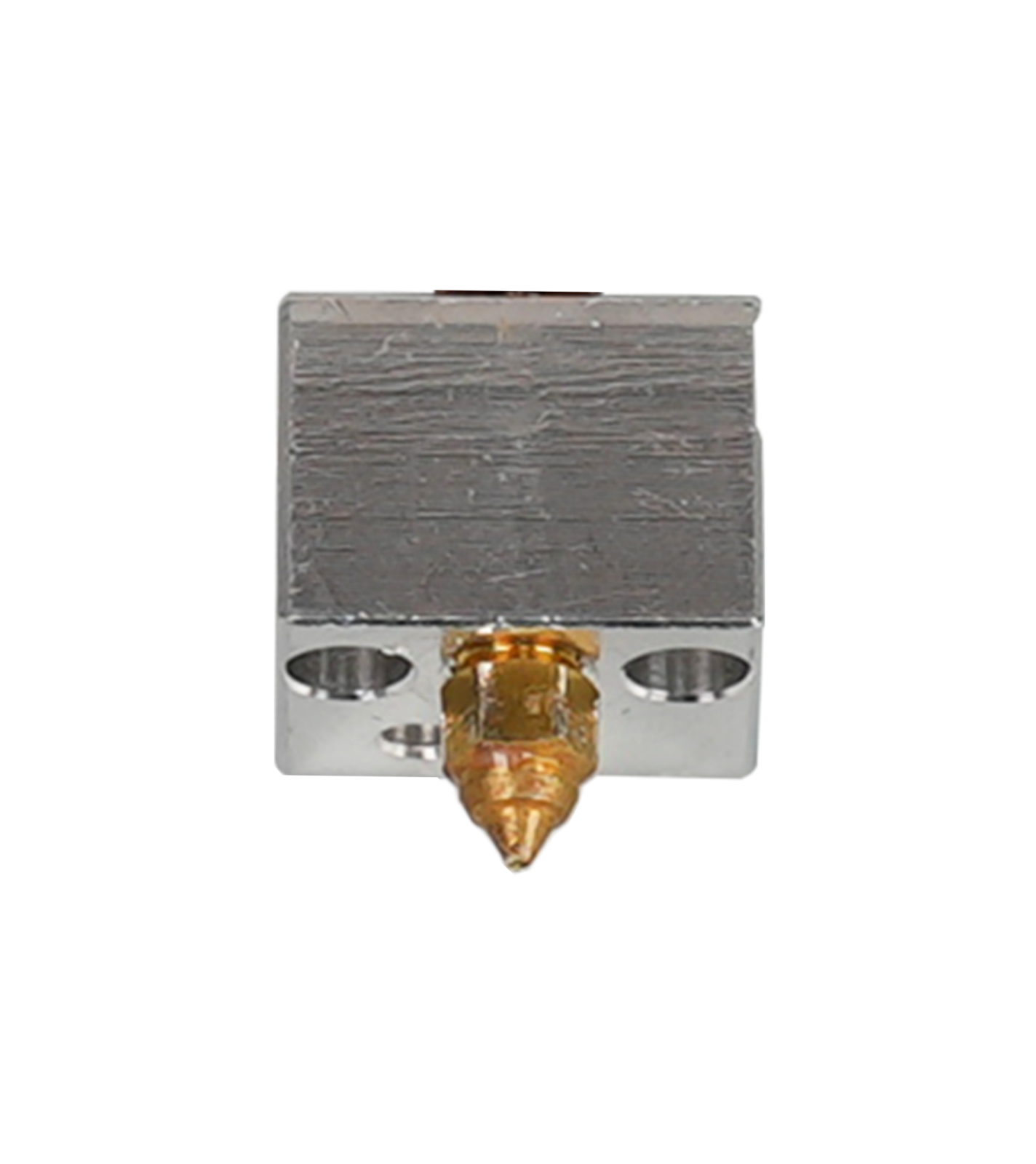
| nozzle assembly | The nozzle assembly has nozzle, heating block, thermistor, throat pipe, silicone case and PTFE tube. | ||
| chamber heater unit | The chamber heater unit is a component that heats the filament until melted. |
 |
|
| nozzle | The nozzle extrudes the melted filament. The most frequently used diameter includes 0.2 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm and 0.8 mm. |
 |
|
| throat pipe | The throat pipe joints the heating block and nozzle to ensure that filament can be extruded through the nozzle successfully. | ||
| heat sink | The heat sink can dissipate heat of throat pipe to prevent the filament from melting too early due to being overheated. | ||
| PTFE tube | The PTFE tube works as a barrier to prevent excess heat from passing to throat pipe, which may influence the extrusion. | ||
| fans | throat cooling fan | The fan is fixed outside the throat pipe to dissipate heat. | |
| model cooling fan | The fan can cool down the extruded filament immediately to ensure the following layers are printed successfully. | ||
| auxiliary part cooling fan | The fan can cool down the auxiliary parts to ensure high-quality cooling effect. | ||
| main board fan | The fan can disperse heat of main board that mainly comes from motor driving. |
 |
|
| main structure | X motor | The X motor controls horizontal move of the printing head. | |
| Y motor | The Y motor controls back-and-forth move of heatbed unit. | ||
| Z motor | The Z motor controls the up-and-down move of printing head. | ||
| power | The power offers the electrical energy of the printer. |
 |
|
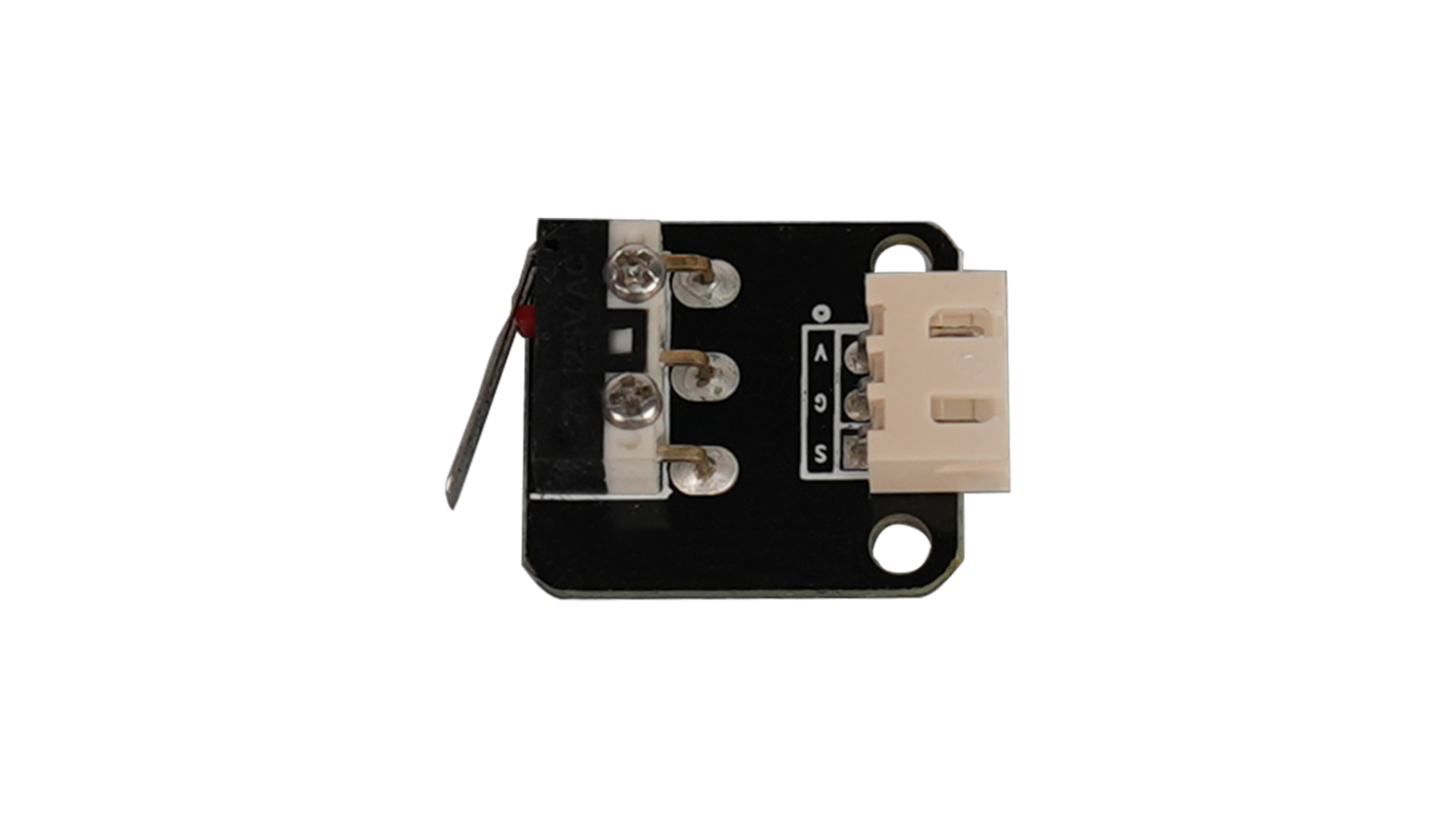
| limit switch | The limit switch is a signal trigger, checking the location of apparatuses. |
 |
|
| proximity sensor | The proximity sensor is used for automatic leveling to check the distance between printing head and hotbed. | ||
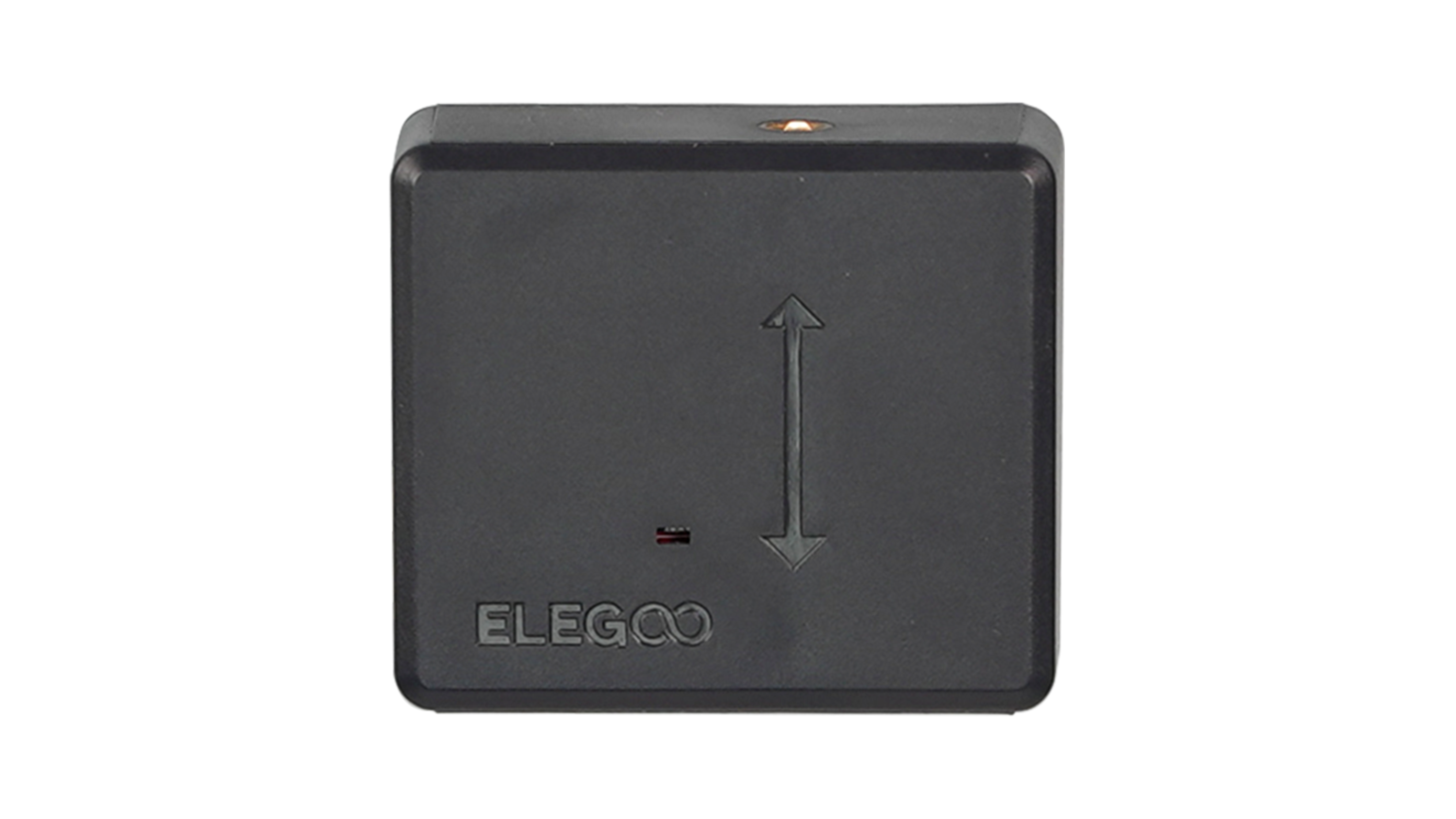
| filament detection module | The filament detection module can sense whether there is any filament going through it. If none, the printer will alarm and suspend printing. |
 |
|
| timing belt | The synchronous belt is a transmission component, driving printing head and hotbed. | ||
| timing pulley | The synchronous pulley has teeth outside. It is used with synchronous belt to fulfill high-precision movement. | ||
| spring | The spring is used to level hotbed. | ||
| knurled nut | The knurled nut is used to fine-tune the operation pulley of the hotbed. | ||
| offset post | Since that the central line of the offset post does not overlap with that of through hole, the offset post can adjust the clearance between pulley and guide rail. | ||
| T-shaped bolt | The T-shaped bolt is a traditional compoent working as Z axis moving systm. | ||
| T-shaped screw | The T-shaped screw is used to move the printing head up and down, ensuring the steady move and precise position of printing head on Z axis. | ||
| sheave assembly | The assembly is used for directing moving components, reduce friction and achieve steady linear moving. | ||
| coupling | The coupling is used to join driving components like motors and screws. | ||
| belt tension adjustment knob | The knob can adjust the belt take-up components and change the tension of belt simultaneously. | ||
| nozzle heater | It is used to heat the nozzle (Neptune 3 series and Neptune 4 and 4 pro use heating rod). | ||
| It is used to heat the nozzle (Neptune 4 Plus and Max use ceramic heating plate). | |||
| thermistor | It is the sensor of temperature that can monitor real-time temperature. | ||
| silicone nozzle cover | The cover protects the nozzle from sticky filament and serves as a insulating layer. | ||
| control system | main board | The main board is the core controlling system of printer. It manages and coordinates the whole printing system. |
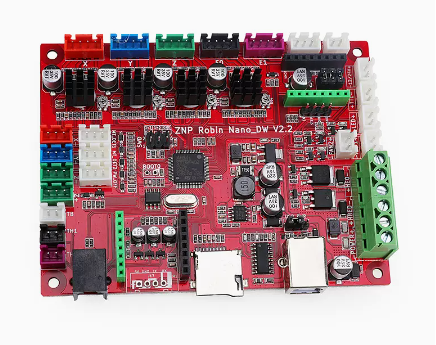 |
| extrusion controlling board | The board safeguards the precision, stability and high quality of printing by controlling extrusion motor and relevant assemblies. | ||
| hotbed | PEI texture board | It is 3D printing board with PEI added into its surface, which can improve the adhesion of models. It is compatible with various filaments. | |
| hotbed leveling | Hotbed leveling is crucial to high-quality printing. If the hotbed is not level, the frist layer of models will be uneven. | ||
| A4 Paper Test Method | 1. Put a piece of A4 paper between hotbed and nozzle; 2. Control the nozzle move to certain height of Z axis; 3. Pull the paper back and forth until there is obvious resistence. |
||
| Mesh Bed Compensation | The mesh bed can compensate the irregularity of hotbed to fulfill the evenness of the first layer. | ||
| automation | auto leveling | The auto leveling makes sure that certain height can be kept. | |
| resonance compensation | A kind of technology can reduce lines on models. | ||
| pressure in advance | The function of pressure in advance can reduce the overflow of filament during non-excrusion process and bulge of corner. | ||
| filament detection | The filament detection can safeguard the continuity of printing. Otherwise, the filament may lost and cause failure of printing. | ||
| resume printing even despite powering off | If the printing breaks off, the printer can resume the printing from where it stops instead of restrating. It is recommended that length of power-off does not exceed that of cool-down of hotbed. | ||
| auxiliary function | observation light | The light is located under the LED light to illuminate the printing area for observation. | |
| head light | It refers to the LED light belt at the top of the printer for illuminating the whole printer. | ||
| touch screen | The touch screen can operate the printer with all functions. | ||
| parts | spool holder | The spool holder is installed on the beam of the frame to place filament. | |
| scraper | The scraper can shovel the models from PEI platform. | ||
| U disk | The U disk saves model files. | ||
| tool package | The tool package includes installation tools and spare parts. | ||
| snipper | The snipper can be used to trim filament and supports. | ||
| needle | The needle can clear the nozzle if it is clogged by filament. | ||
| lubricating oil | The lubricating oil has low stickness. It is exclusively used for guide rail maintenance. | ||
| lubricating grease | The lubricating grease has high stickness. It is used for the maintenance of double-axis guide rail and bolt. | ||
| thermal paste | It is used for improve the performance of heat conduction. | ||
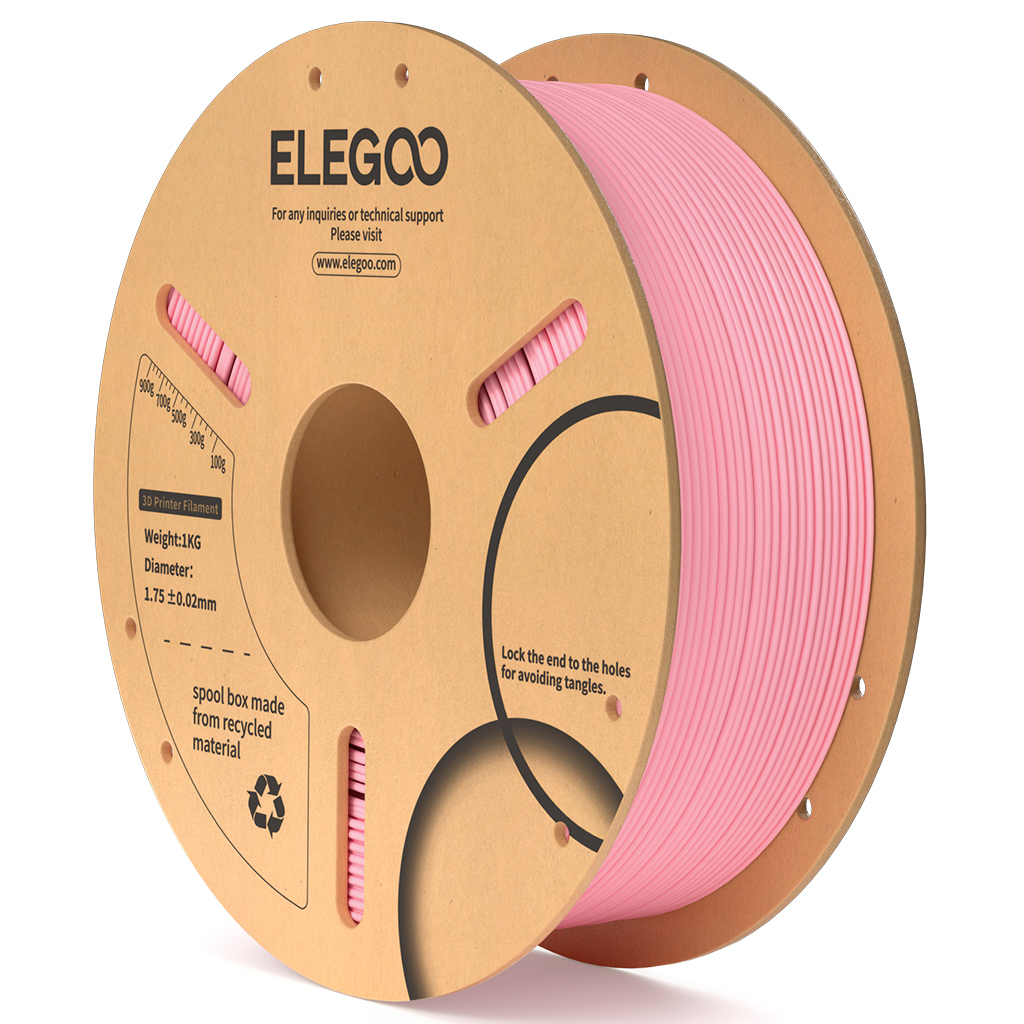
| filament | ELEGOO PLA | PLA belongs to biodegradable thermoplastic polymer. It is the filament with basic performance. |
 |
| ELEGOO PLA PRO | PLA PRO is upgraded on the basis of PLA. It is has high compatibility with various printers. | ||
| ELEGOO PLA+ | PLA+ has stronger performance of PLA with is strong toughness. | ||
| ELEGOO RAPID PLA+ | RAPID PLA+ is compatible with high-speed printers. | ||
| ELEGOO PLA MATTE | PLA MATTE is the filament of macaron colour. | ||
| ELEGOO PLA SILK | PLA SILK refers to the filament with silk-like texture and very high surface gloss. | ||
| ELEGOO PETG PRO | PETG PRO has high toughness and durability, applicable to components with high impact resistance. | ||
| ELEGOO RAPID PETG | RAPID PETG can meet the demands of high-speed printers. | ||
| ELEGOO TPU | TPU is soft filament with super toughness. | ||
| ELEGOO ASA | ASA is industrial plastics, analogous to ABS. It has better high-temperature resistance and ultraviolet resistance. | ||
| print quality | string / stringing | The string refers to the excess filament oozing from the printing models and stacking around the nozzle. | |
| ringing | Ringing, presented like waves, often appears around the sharp corners and angles on the model surface. | ||
| clog / clogging; jam / janmming |
Clogging refers to that the nozzle or extrusion device is clogged by filament so that the printers cannot extrude and feed the filament successfully. | ||
| warping | Warping refers to that edge of models is warped, leading to deformation of bottom layers. | ||
| oozing | Oozing refers to that as nozzle assemblies are installed improperly, the melted filament is oozing out of the gaps. | ||
| split-level layers | It means that the model has split-level layers. | ||
| Spaghetti | It refers to that the extruded filament scattered like spaghetti due to that the filament failed to stick on the hotbed or that the filament is extruded randomly as the model dropped out. | ||
| wear | The wear refers to that the parts of printers rub with each other and wears away. | ||
| layer lines | The irregular grain on the surface of models. | ||
| insufficient-extrusion | It means that because the nozzle did not extrude enough filament, so the model has big gaps and hollowed area. | ||
| over-extrusion | It means that because the nozzle extrude excessive filament, so the model bulge on its surface. | ||
| insufficient heat dissopation; insufficient cooling |
If the model is positioned improperly, the cooling fans will not cover some part of the model, and then the heat cannot dissipate in time. That may cause damage on the surface. | ||
| seam | The seam refers to the beak at the beginning and end of layers when printing curved surface. |